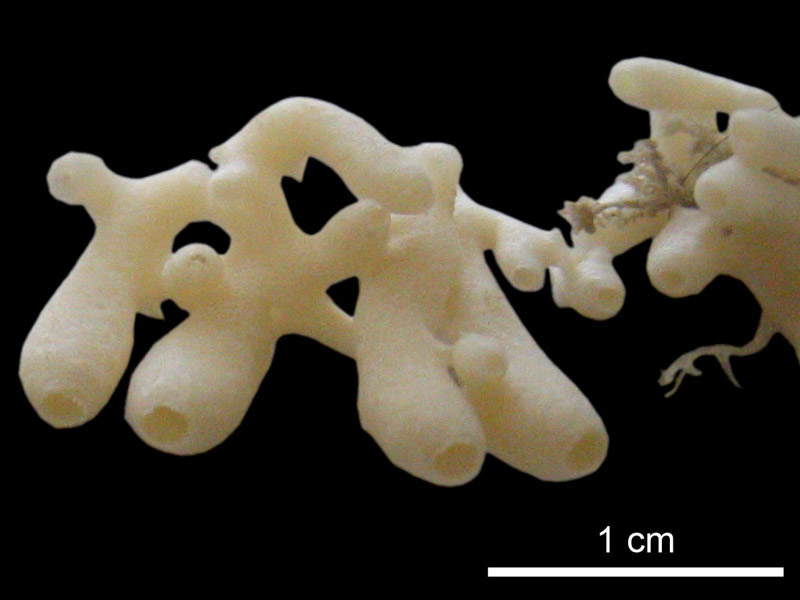
| Tubes, branching and anastomosing esp. In the proximal part. |
| One terminal losculum at the distal end of each tube, smaller in diameter than the tube. |
| Soft |
| No surface ornamentation |
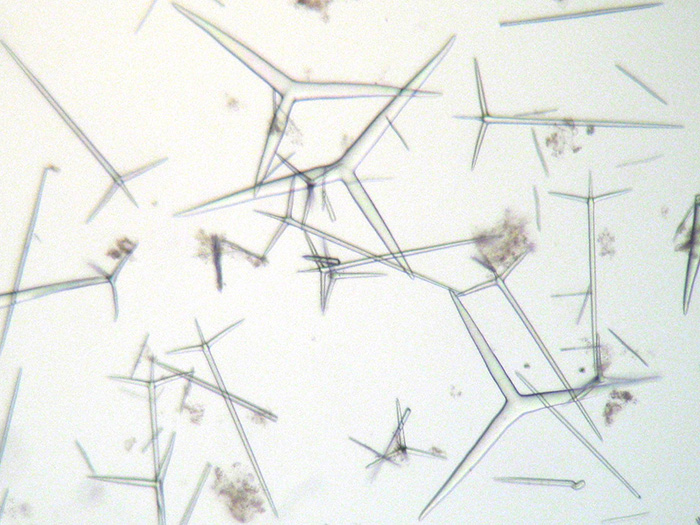
| With an inarticulated skeleton supported by the apical actines of sub-atrial sagittal tetractines and nail-shaped triactines. Nail-shaped triactines pointing with their ÔunpairedÕ actines towards the cortex, their distal part sometimes penetrating the cortical tangential layer of sagittal triactines. The unpaired actines of the sub- atrial triactines do not extend to the cortex. The atrial skeleton is formed by sagittal tetractines with their curved free actines pointing towards and into the atrium. |
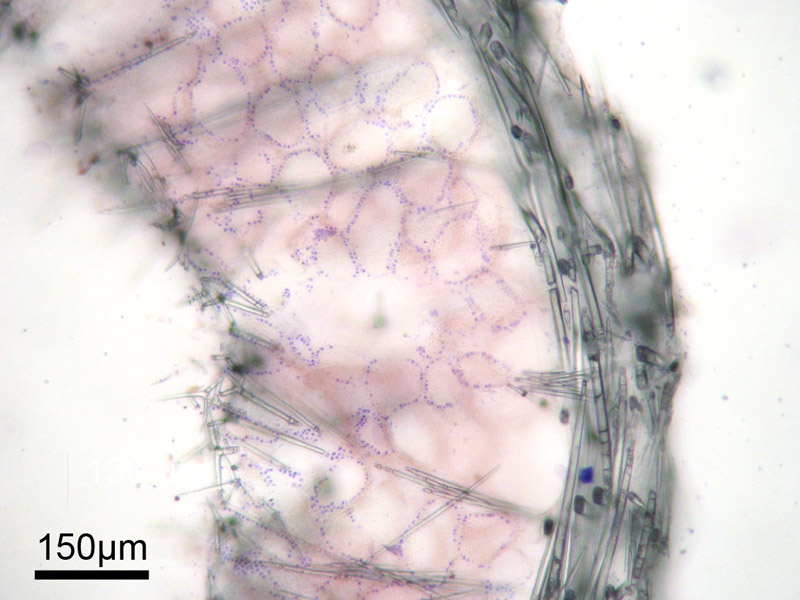
| A distinct cortex of tangentially arranged sagittal triactines and perpendicularly arranged microdiactines. |
| Cortical sagittal triactines are thick, with more-or-less cylindrical actines. Paired actines have a size of 225.8-(282.4)-351.9 um, unpaired actines 217.5-(278.9)-355 um. Choanosomal nail-shaped triactines (with strongly reduced paired actines) are 226.4-(288.3)-308.9 um long. Subatrial sagittal tetractines delimit the choanosome towards the atrial skeleton with their regular basal triradiate system (41.7-(70.3)-98 um), and their elongated apical actine (289.4-(305.4)-335.3 um long) forms the proximal part of the choanoskeleton. All actines are more-or-less cylindrical, whereas the longer apical actine has a conical tip. Atrial tetractines are sagittal with their free and curved apical actine ( ) protruding into the atrium. The the basal triradiate actines are () um long. |
| Cortical microdiactines are 55.2-(75.8)-97.5 um long. They are slender, tapering towards both ends, with a slight thickening about 66% toward their proximal end, and are often finely spined. |