Morphological description (show/hide)
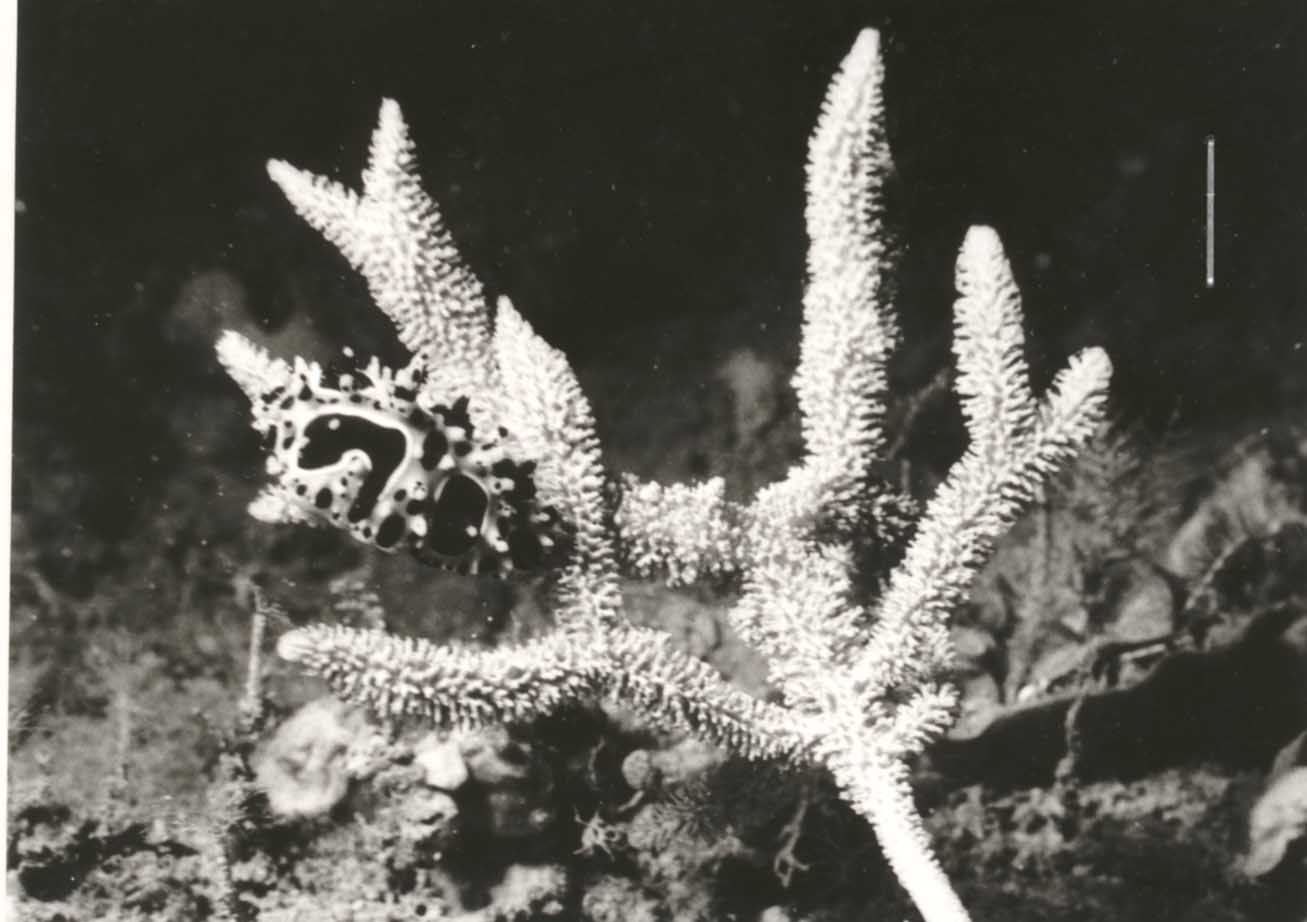
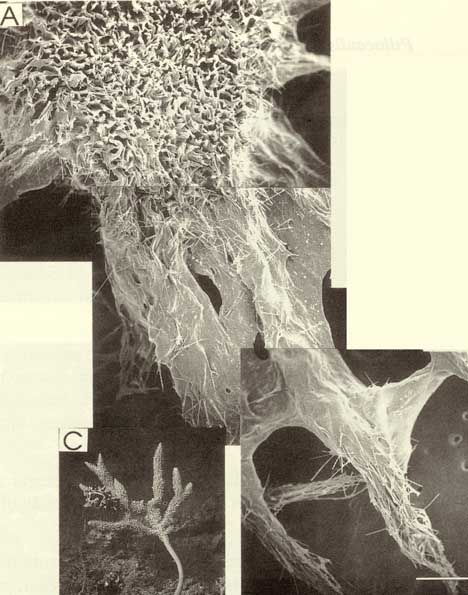
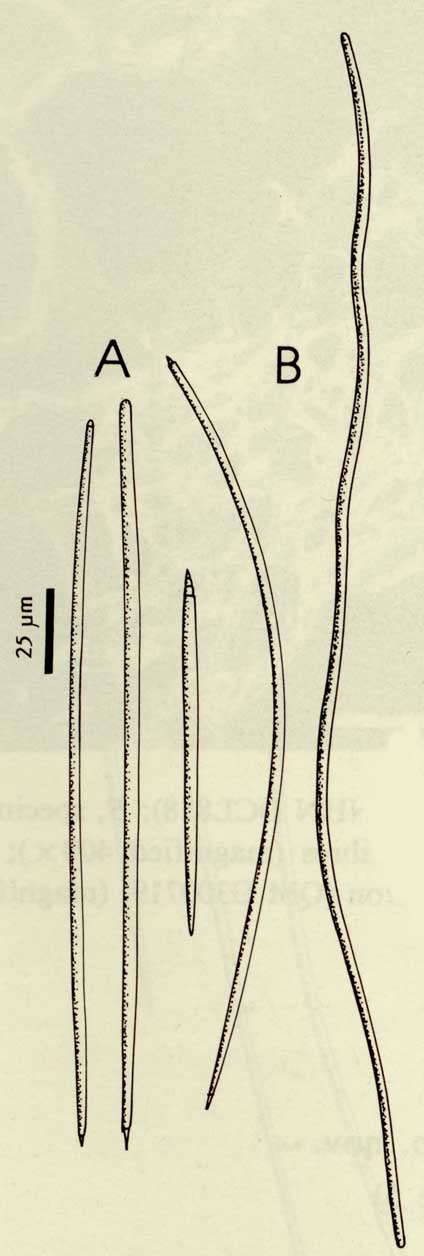
| Arborescent, bifurcate branching, 200mm long, 70mm maximum lateral branch span, with thin, cylindrical branches, 27-60mm long, 5-17mm wide including papillae, tapering towards pointed branch tips, with long, unornamented stalk, 75mm long, 4mm diameter, and expanded basal attachment, 13mm diameter. | | Live colouration pale yellow-brown (Munsell 2 | | Heavily ornamented, papillose surface, with long, close-set, sharply pointed, soft papillae, 2-4mm long, 0.5-1mm diameter, up to 2mm apart, tips of papillae bifurcate and/or hispid, bases of adjacent papillae interconnected by membranous ridges running longitudinally along branches, slightly elevated above surface of sponge. | | Skeleton structure plumo-reticulate, with clearly differentiated axial and extra-axial regions, and a compressed axial skeleton. Compressed region of skeleton occupies only about half (2-3mm) of branch diameter (3-5mm), composed of heavy, bulbous spongin fibres, with individual fibres only about 100um long, 50-70um diameter, together forming a close-set reticulation and producing small oval meshes, 50-90um diameter, axial fibres cored by uni-, pauci- or multispicular tracts of thin megascleres, occupying only a small proportion of fibre diameter. Abundant, lightly pigmented collagen in mesohyl of axial skeleton. Extra-axial skeleton extensive, including area immediately surrounding axis of branches (1-2mm diameter) as well as elongated, slender skeletal columns (=papillae, up to 4mm long). Extra-axial skeleton composed of primary and secondary fibre systems, differentiated mainly by presence or absence of coring spicules, both fibre systems composed of heavy spongin fibres, with individual fibres up to 300um long, 40-60um diameter, producing a relatively wide, elongate mesh reticulation, 110-170um mesh diameter, ascending extra-axial fibres cored by multispicular, plumose columns of choanosomal styles, with spicule tracts becoming heavier towards peripheral skeleton [eventually terminating in plumose brushes which may or may not protrude through surface (tips of papillae, versus between papillae, respectively)]. Many (but not all) transverse, connecting fibres in extra-axial skeleton uni- or aspicular, with long exceedingly slender strongyles (although these were invariably broken in situ, and consequently were not observed in spicule preparations). Collagen abundant and slightly more darkly pigmented in extra-axial region, choanocyte chambers not observed. | | Fleshy, membranous ectosome, without specialised spicules, with sparse detritus embedded in and on surface, with heavy collagenous, aspicular matrix, 150-200um wide, lying between papillae (= surface ridges) and on sides of papillae, apex of each papilla has plumose brushes of choanosomal styles, in small multispicular bundles, protruding for short distances, up to 200um from surface. | | Two categories of spicules present, clearly differentiated in morphology but not obviously localised to any particular region of skeleton. Few transverse, connecting fibres contain a single, long, thin, sinuous strongyle, but these spicules are rare (424-(448.2)-488 x 1.5-(1.8)-2). Majority of spicules are styles or styloids, short or long, slender, straight or slightly curved asymmetrically, with evenly rounded or tapering mucronate bases, and hastate, fusiform or stepped points (134-(268.4)-328 x 2.5-(3.4)-5). | | Nil. |
|